2024 |
||
| 1. | 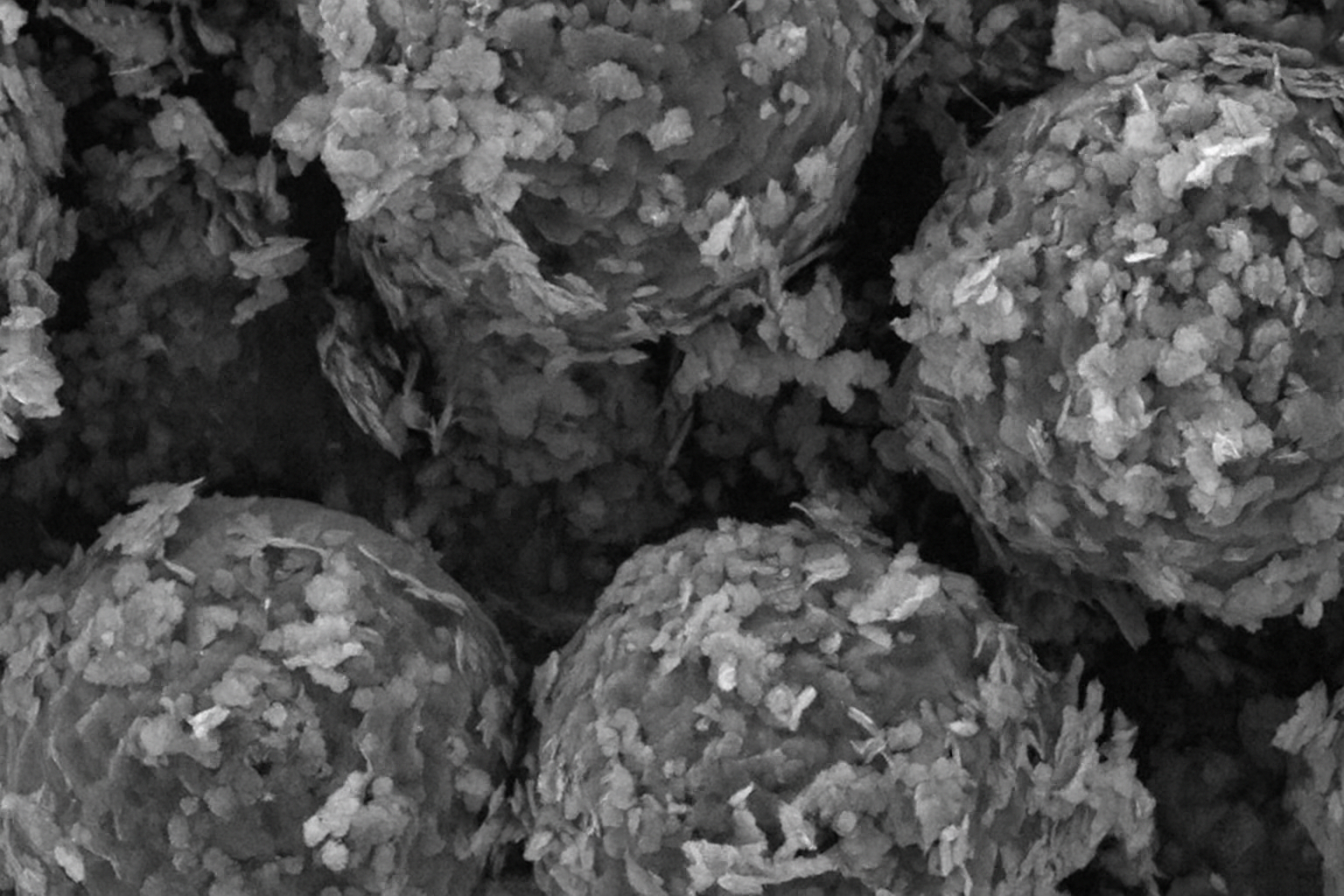 | Y. Cao; C. I. Sathish; Z. Li; M. I. Ahmed; V. Perumalsamy; C. Cao; C. Yu; B. Wijerathne; A. J. Fleming; L. Qiao; S. Wang; J. Yi Plastics adsorption and removal by {2D} ultrathin iron oxide nanodiscs: From micro to nano Journal Article In: Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 497, pp. 154610, 2024, ISBN: 1385-8947. Abstract | Links | BibTeX | Tags: Nanotechnology, Raman @article{J24c,The escalation of microplastics/nanoplastics (MPs/NPs) contamination in aqueous systems has ignited considerable concern. Magnetic separation has emerged as a promising remedy for the removal of these pollutants, owing to its notable removal efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmentally friendly attributes. This study presents the utilization of ultra-thin magnetic Fe3O4 nanodiscs (NDs) for the adsorption and separation of MPs/NPs. Investigations revealed that these NDs could effectively adsorb/remove MPs/NPs across a spectrum ranging from micro- to nano-scale, exhibiting a notable adsorption capacity of 188.4 mg g−1. Mechanistically, MPs/NPs adsorption was driven by both electrostatic and magnetic forces originating from the vortex domain of NDs, which can be well described by pseudo-first-order and Sips models. Furthermore, the NDs exhibited outstanding reusability, maintaining over 90 % removal efficiency even after undergoing five cycles. This research introduces a cost-effective method for the separation of MPs/NPs, representing a significant stride in wastewater treatment methodologies. |
2024 |
||
| 1. |  | Plastics adsorption and removal by {2D} ultrathin iron oxide nanodiscs: From micro to nano Journal Article In: Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 497, pp. 154610, 2024, ISBN: 1385-8947. |
